After a rabid animal is euthanized the head of the animal is sent into a qualified laboratory for testing. Because the rabies virus spreads throughout the brain, it is required to test two different areas of the brain for the presence of Negri bodies. The cerebellar tissue should be tested along with the brain stem at either the pons, medulla, or midbrain. The tissue sample needs to be prepared by fixation, dehydration, embedding, sectioning, and staining. The brain sample is cut in cross section and the two tissues from different locations should be stained with reagent. Two reagents are prepared using different sources from FITC-labeled anti-rabies reagents. Positive and negative control slides are then prepared from rabid animals and normal animals to compare to the sample being tested. The tissue sample is then observed at 200X under a fluorescence microscope. In the brain of a rabid animal the presence of intracytoplasmic inclusions of various shapes is characteristic of the virus. The staining intensity and antigen distribution is noted for each slide and compared to the positive and negative controls. The process is repeated and the new slides are compared again to solidify the result. The animal is then classified as positive or negative for the rabies virus. If the animal is considered positive for rabies the leftover brain tissue should be sent to another laboratory for confirmation and virus typing (Protocol).
Although fluorescence microscopy is the most common way of detecting rabies, general microscopy can also be used. Typically this is done when rabies is not suspected and other methods of rabies testing has not been performed. Staining with Hematoxylin and Eosin is used to locate encephalomyelitis or inflammation in the sample. The identification of mononuclear infilitration, perivascular cuffing of lymphocytes or polymorphonuclear cells, lymphocytic foci, babes nodules consisting of glial cells, and Negri bodies is used to detect rabies using general histopathology (Rabies - CDC).
 |
The brain tissue is tested for the presence
of Negri bodies at the cerebellum or brain stem. (Protocol) |
 |
The brain stem is made up of the midbrain, pons and medulla.
(Protocol)
|
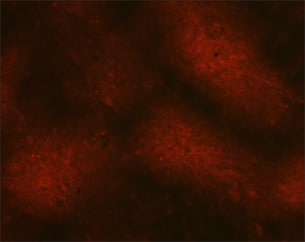 |
| Direct fluorescent antibody test that is negative for the rabies virus. (Rabies - CDC) |
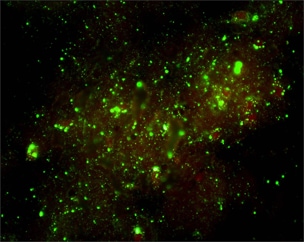 |
| Direct fluorescent antibody test that is positive for the rabies virus. (Rabies - CDC) |
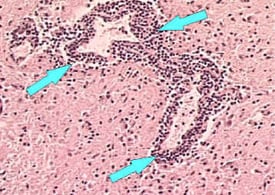 |
| Brain tissue showing perivascular cuffing around a blood vessel. (Rabies- CDC) |
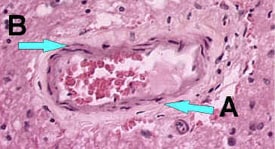 |
| Brain tissue without inflammation around the blood vessels. (Rabies - CDC) |
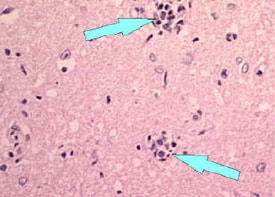 |
| Babes Nodules (Rabies - CDC) |
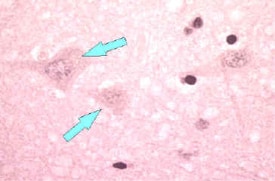 |
| Brain tissue neuron without Negri bodies. (Rabies - CDC) |
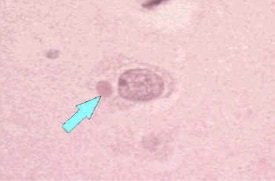 |
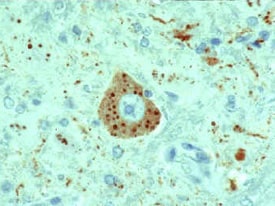
| Brain tissue with Negri bodies. (Rabies - CDC) |
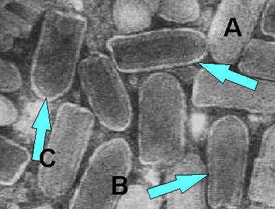 |
Electron Microscopy is used to view the ultrastructure of the Rabies virus. The virus belongs to the Rhabdovirus family which has a bullet shaped structure.
(Rabies - CDC)
|
No comments:
Post a Comment